
2024年您產品必備的10大AI API推薦
Function Call功能指的是語言模型在生成回答時,通過調用外部API接口來獲取數據或執行操作。這種功能不僅擴展了模型的應用場景,還提升了其智能化水平。通過與外部系統的互動,模型可以實時獲取最新的信息、執行復雜任務,并提供更加精準和實用的回答。
后續內容將以ChatGLM-6B為例來介紹Function Call。
Function Call功能在多個實際應用場景中發揮重要作用,包括但不限于:
3. 如何讓模型具備Function Call
要讓模型具備Function Call功能,需要通過設計和訓練包含API調用示例的數據集,使模型學習如何在適當的上下文中生成API調用指令。模型訓練時結合這些示例進行定制化訓練,并通過強化學習優化調用策略。確保數據的一致性和實時更新,以適應API的變化,同時收集用戶反饋進行持續改進,從而實現模型對API調用的準確生成和有效處理。
基于Function Call的ChatGLM-6B對話格式:
<|system|>
Answer the following questions as best as you can. You have access to the following tools:
[
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {"type": "string"},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
]
<|user|>
今天北京的天氣怎么樣?
<|assistant|>
好的,讓我們來查看今天的天氣
<|assistant|>get_current_weather
tool_call(location="beijing", unit="celsius")
<|observation|>
{"temperature": 22}
<|assistant|>
根據查詢結果,今天北京的氣溫為 22 攝氏度。上面對話格式說明:

ChatGLM3 是智譜AI和清華大學 KEG 實驗室聯合發布的對話預訓練模型。ChatGLM3-6B 是 ChatGLM3 系列中的開源模型,在保留了前兩代模型對話流暢、部署門檻低等眾多優秀特性的基礎上,ChatGLM3-6B 引入了如下特性:
注意:目前只有 ChatGLM3-6B 模型支持工具調用,而 ChatGLM3-6B-Base 和 ChatGLM3-6B-32K 模型不支持。
a. 多模態預訓練
a. 工具集成
b. 工具調用接口
a. 多任務學習
b. 示例學習
a. 上下文感知
b. 決策策略
總之,在ChatGLM-6B中,函數/工具調用(Function Call)通過以下步驟實現:
本部分將通過代碼來實現ChatGLM-6B調用天氣接口來獲取查詢地的天氣情況。
ChatGLM-6B模型權重下載地址(下面任選一個):
代碼包括兩個部分: 工具定義代碼和ChatGLM-6B調用工具代碼。由于我將ChatGLM-6B權重下載到了本地,具體路徑為:/root/autodl-tmp/chatglm3-6b提示:將下面代碼路徑/root/autodl-tmp/chatglm3-6b替換為你的路徑。工具定義代碼(tool_register.py)
"""
這段代碼是工具注冊的部分,通過注冊工具,讓模型實現工具調用
"""
import inspect
import traceback
from copy import deepcopy
from pprint import pformat
from types import GenericAlias
from typing import get_origin, Annotated
_TOOL_HOOKS = {}
_TOOL_DESCRIPTIONS = {}
def register_tool(func: callable):
tool_name = func.__name__
tool_description = inspect.getdoc(func).strip()
python_params = inspect.signature(func).parameters
tool_params = []
for name, param in python_params.items():
annotation = param.annotation
if annotation is inspect.Parameter.empty:
raise TypeError(f"Parameter {name} missing type annotation")
if get_origin(annotation) != Annotated:
raise TypeError(f"Annotation type for {name} must be typing.Annotated")
typ, (description, required) = annotation.__origin__, annotation.__metadata__
typ: str = str(typ) if isinstance(typ, GenericAlias) else typ.__name__
if not isinstance(description, str):
raise TypeError(f"Description for {name} must be a string")
if not isinstance(required, bool):
raise TypeError(f"Required for {name} must be a bool")
tool_params.append({
"name": name,
"description": description,
"type": typ,
"required": required
})
tool_def = {
"name": tool_name,
"description": tool_description,
"params": tool_params
}
_TOOL_HOOKS[tool_name] = func
_TOOL_DESCRIPTIONS[tool_name] = tool_def
return func
def dispatch_tool(tool_name: str, tool_params: dict) -> str:
if tool_name not in _TOOL_HOOKS:
return f"Tool {tool_name} not found. Please use a provided tool."
tool_call = _TOOL_HOOKS[tool_name]
try:
ret = tool_call(**tool_params)
except:
ret = traceback.format_exc()
return str(ret)
def get_tools() -> dict:
return deepcopy(_TOOL_DESCRIPTIONS)
# tools Definitions
@register_tool
def random_number_generator(
seed: Annotated[int, 'The random seed used by the generator', True],
range: Annotated[tuple[int, int], 'The range of the generated numbers', True],
) -> int:
"""
Generates a random number x, s.t. range[0] <= x < range[1]
"""
if not isinstance(seed, int):
raise TypeError("Seed must be an integer")
if not isinstance(range, tuple):
raise TypeError("Range must be a tuple")
if not isinstance(range[0], int) or not isinstance(range[1], int):
raise TypeError("Range must be a tuple of integers")
import random
return random.Random(seed).randint(*range)
@register_tool
def get_weather(
city_name: Annotated[str, 'The name of the city to be queried', True],
) -> str:
"""
Get the current weather for city_name
"""
if not isinstance(city_name, str):
raise TypeError("City name must be a string")
key_selection = {
"current_condition": ["temp_C", "FeelsLikeC", "humidity", "weatherDesc", "observation_time"],
}
import requests
try:
resp = requests.get(f"https://wttr.in/{city_name}?format=j1")
resp.raise_for_status()
resp = resp.json()
ret = {k: {_v: resp[k][0][_v] for _v in v} for k, v in key_selection.items()}
except:
import traceback
ret = "Error encountered while fetching weather data!\n" + traceback.format_exc()
return str(ret)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# print(dispatch_tool("random_number_generator", {"seed": 2024, "range":(1, 10)}))
print(get_tools())
大模型調用工具代碼:
"""
This demo script is designed for interacting with the ChatGLM3-6B in Function, to show Function Call capabilities.
"""
import os
import platform
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
from tool_register import get_tools, dispatch_tool
import json
tools = get_tools()
print(tools)
MODEL_PATH = os.environ.get('MODEL_PATH', '/root/autodl-tmp/chatglm3-6b')
TOKENIZER_PATH = os.environ.get("TOKENIZER_PATH", MODEL_PATH)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(TOKENIZER_PATH, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(MODEL_PATH, trust_remote_code=True, device_map="auto").eval()
os_name = platform.system()
clear_command = 'cls' if os_name == 'Windows' else 'clear'
stop_stream = False
tools = get_tools()
system_item = {
"role": "system",
"content": "Answer the following questions as best as you can. You have access to the following tools:",
"tools": tools
}
def main():
past_key_values, history = None, [system_item]
role = "user"
global stop_stream
print("歡迎使用 ChatGLM3-6B 模型,輸入內容即可進行對話,clear 清空對話歷史,stop 終止程序")
while True:
query = input("\n用戶:") if role == "user" else query_rt
if query.strip() == "stop":
break
if query.strip() == "clear":
past_key_values, history = None, [system_item]
role = "user"
os.system(clear_command)
print("歡迎使用 ChatGLM3-6B 模型,輸入內容即可進行對話,clear 清空對話歷史,stop 終止程序")
continue
print("\nChatGLM:", end="")
# 目前 ChatGLM3-6B 的工具調用只支持通過 chat 方法,不支持 stream_chat 方法。
response, history = model.chat(tokenizer, query, history=history, role=role)
print(response, end="", flush=True)
# 這里 role="observation" 表示輸入的是工具調用的返回值而不是用戶輸入,不能省略。
if isinstance(response, dict):
name = response['name']
param = response['parameters']
print(f"開始調用API:{name}", end="")
rt = dispatch_tool(name, param)
query_rt = json.dumps(rt, ensure_ascii=False)
role = "observation"
else:
role = "user"
print(response, end="", flush=True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()執行結果:
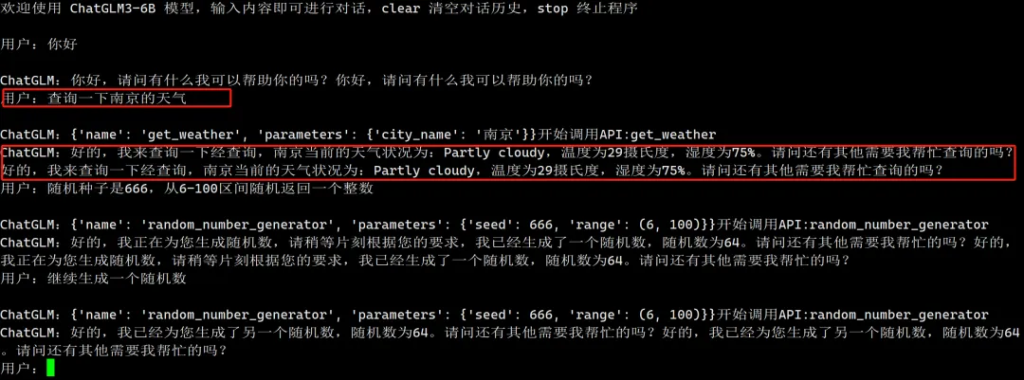
Function Call功能通過API接口的引入,顯著提升了語言模型的智能化水平。以ChatGLM-6B為例,模型通過多模態預訓練、工具接口集成、請求生成和結果整合等步驟,實現了在對話中智能地調用外部工具。這種功能不僅提升了模型處理實時數據的能力,還擴展了其應用范圍,增強了用戶交互體驗。未來,隨著技術的進一步發展和挑戰的解決,Function Call功能將在語言模型的智能化進程中發揮更大的作用,為用戶提供更為精準和實用的服務。
文章轉自微信公眾號@大廠小僧
、