大語言模型,像 ChatGPT, Llama 等已經席卷全球,從上圖的數據可以看出,ChatGPT 花了 5 天時間就達到了 100 萬用戶。而 Netflix 則花了近 4 年的時間。本文將使用 Gin 和 Langchain 教你快速構建一套 LLM API。
Gin[1]?是一個用于使用GoLang構建API的現代、快速的Web框架。它被設計為易于使用、高效且性能出色,利用了GoLang并發的強大能力,以實現極高的吞吐量。
LangChain[2]?是一個用于開發由語言模型驅動的應用程序的框架。它旨在讓開發者輕松地連接到一個 LLM,并使用戶能夠為 LLM 提供額外的上下文。簡單來說,Langchain使LLM模型能夠基于在線、文檔或其他數據源中最新的信息生成響應。
首先確保已經安裝了 Golang 的開發環境,其次需要下面幾個依賴包:
$ go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin
$ go get github.com/tmc/langchaingo
$ go get github.com/google/uuid
$ go get golang.org/x/exp@v0.0.0-20230713183714-613f0c0eb8a1routes/structs.go)GenerateVacationIdeaRequest 是用戶將提供給我們的內容,以便我們為他們創建 vacation idea。我們希望用戶告訴我們他們喜歡的季節、他們可能有的任何愛好,以及他們的度假預算是多少。我們可以在后面將這些輸入提供給 LLM。
GenerateVacationIdeaResponse 是我們將返回給用戶的內容,表示想法正在生成中。Langchain 可能需要一些時間來生成響應,我們不希望用戶永遠等待他們的HTTP調用返回。因此,我們將使用 goroutines(稍后會詳細介紹!),用戶可以在幾秒鐘后檢查想法是否已完成。
GenerateVacationIdeaResponse 反映了這一點,包含兩個字段:
GetVacationIdeaResponse 是當用戶查詢想法或其狀態時我們將返回給用戶的內容。幾秒鐘后,用戶會說 “嗯,想法已經完成了嗎?”然后可以查詢我們的API。GetVacationIdeaResponse 具有與 GenerateVacationIdeaResponse 相同的字段,但添加了一個想法字段,當生成完成時 LLM 將填寫該字段。
type GenerateVacationIdeaRequest struct {
FavoriteSeason string json:"favorite_season"
Hobbies []string json:"hobbies"
Budget int json:"budget"
}
type GenerateVacationIdeaResponse struct {
Id uuid.UUID json:"id"
Completed bool json:"completed"
}
type GetVacationIdeaResponse struct {
Id uuid.UUID json:"id"
Completed bool json:"completed"
Idea string json:"idea"
}routes/vacation.go)現在我們的請求和響應模式已經確定,我們可以寫路由了。
GetVacationRouter 函數接受一個gin路由器作為輸入,并為其添加一個新的路由器組,路徑前綴為 /vacation。因此,我們添加到路由器的任何端點都將具有 /vacation前綴。然后我們添加兩個端點:
/create?端點將啟動一個goroutine,調用 langchain 和 openAI。它將返回一個?GenerateVacationIdeaResponse?給調用者,以便他們稍后可以檢查其狀態。他們可以通過?/:id?端點來檢查該想法的狀態。這將返回一個?GetVacationIdeaResponse。如果想法已經完成生成,它將包含一個id、一個想法,并且?completed?標志將設置為true。否則,它將包含一個id、一個空想法,并且?completed?標志將設置為 false。
package routes
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/afoley587/52-weeks-of-projects/07-golang-gin-langchain/chains"
"github.com/google/uuid"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func generateVacation(r GenerateVacationIdeaRequest) GenerateVacationIdeaResponse {
// First, generate a new UUID for the idea
id := uuid.New()
// Then invoke the GeneateVacationIdeaChange method of the chains package
// passing through all of the parameters from the user
go chains.GeneateVacationIdeaChange(id, r.Budget, r.FavoriteSeason, r.Hobbies)
return GenerateVacationIdeaResponse{Id: id, Completed: false}
}
func getVacation(id uuid.UUID) (GetVacationIdeaResponse, error) {
// Search the chains database for the ID requested by the user
v, err := chains.GetVacationFromDb(id)
// If the ID didn't exist, handle the error
if err != nil {
return GetVacationIdeaResponse{}, err
}
// Otherwise, return the vacation idea to the caller
return GetVacationIdeaResponse{Id: v.Id, Completed: v.Completed, Idea: v.Idea}, nil
}
func GetVacationRouter(router *gin.Engine) *gin.Engine {
// Add a new router group to the gin router
registrationRoutes := router.Group("/vacation")
// Handle the POST to /create
registrationRoutes.POST("/create", func(c *gin.Context) {
var req GenerateVacationIdeaRequest
err := c.BindJSON(&req)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"message": "Bad Request",
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, generateVacation(req))
}
})
// Handle the GET to /:id
registrationRoutes.GET("/:id", func(c *gin.Context) {
id, err := uuid.Parse(c.Param("id"))
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"message": "Bad Request",
})
} else {
resp, err := getVacation(id)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusNotFound, gin.H{
"message": "Id Not Found",
})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, resp)
}
}
})
// Return the updated router
return router
}現在我們可以將路由添加到我們的 API 中了。我們只需要實例化一個 Gin engine,將我們的路由添加到其中,然后運行即可。
import (
"github.com/afoley587/52-weeks-of-projects/07-golang-gin-langchain/routes"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
routes.GetVacationRouter(r)
r.Run()
}現在我們已經為 API 設置了場景。現在,我們需要一種與我們的 LLM 進行交流的方法(或者至少向它提問)。
讓我們定義一個“數據庫”來存儲所有生成的想法。Vacations 是我們的度假“數據庫”。我在數據庫中加了引號,因為這只是一個在整個包中共享的切片。理想情況下,這應該是一種更持久、更穩定、更可擴展的存儲形式,但是本文僅做演示,切片就夠用了。Vacations 是一個Vacation 結構體的切片。我們的 Vacation 結構體只是一個數據持有者。它保存了正在進行和最終的度假對象。它具有我們之前討論過的GetVacationIdeaResponse相同的字段,但我更喜歡將它們分開,這樣可以更容易地解耦這些代碼片段。
我們需要向想要使用這個包的人提供兩種方法:
接下來,我們需要一些實際創建想法并將它們存儲到我們的數據庫中的東西。
GeneateVacationIdeaChange是我們最終開始調用langchain的地方。它接受幾個參數:
首先,我們需要實例化我們的 LLM 模型(這里我們使用 openai )。然后我們需要創建一些 prompts。我們創建一個系統提示以傳遞給 LLM。系統提示是應用程序或系統提供的指令或信息,用于指導對話。系統提示有助于設置上下文和指導 LLM 如何響應人類提示。
一個人類消息和模板遵循著相同的思路。我們可以把它想象成一個聊天應用程序。系統提示有助于設置聊天機器人。人類提示是用戶會問它的內容。
現在模板已經建立,我們可以通過首先創建聊天提示模板來創建聊天提示。為此,我們使用 FormatMessages 方法將用戶提供的值插入到我們的模板中。現在所有內容都以字符串格式進行了模板化。我們將創建LLM消息內容,這是我們的LLM將期望作為輸入的內容。最后,我們可以使用 GenerateContent 調用我們的 LLM。GenerateContent 的輸出將是從 OpenAI API 返回的結果,但我們只關心 LLM 生成的內容。內容是 LLM 生成的字符串響應,類似于 ChatGPT 窗口中返回的響應。
package chains
import (
"context"
"errors"
"log"
"strings"
"github.com/google/uuid"
"github.com/tmc/langchaingo/llms"
"github.com/tmc/langchaingo/llms/openai"
"github.com/tmc/langchaingo/prompts"
"golang.org/x/exp/slices"
)
type Vacation struct {
Id uuid.UUID json:"id"
Completed bool json:"completed"
Idea string json:"idea"
}
var Vacations []*Vacation
func GetVacationFromDb(id uuid.UUID) (Vacation, error) {
// Use the slices package to find the index of the object with
// matching ID in the database. If it does not exist, this will return
// -1
idx := slices.IndexFunc(Vacations, func(v *Vacation) bool { return v.Id == id })
// If the ID didn't exist, return an error and let the caller
// handle it
if idx < 0 {
return Vacation{}, errors.New("ID Not Found")
}
// Otherwise, return the Vacation object
return *Vacations[idx], nil
}
func GeneateVacationIdeaChange(id uuid.UUID, budget int, season string, hobbies []string) {
log.Printf("Generating new vacation with ID: %s", id)
// Create a new vacation object and add it to our database. Initially,
// the idea field will be empty and the completed flag will be false
v := &Vacation{Id: id, Completed: false, Idea: ""}
Vacations = append(Vacations, v)
// Create a new OpenAI LLM Object
ctx := context.Background()
llm, err := openai.New()
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error: %v", err)
return
}
// Create a system prompt with the season, hobbies, and budget parameters
// Helps tell the LLM how to act / respond to queries
system_message_prompt_string := "You are an AI travel agent that will help me create a vacation idea.\n" +
"My favorite season is {{.season}}.\n" +
"My hobbies include {{.hobbies}}.\n" +
"My budget is {{.budget}} dollars.\n"
system_message_prompt := prompts.NewSystemMessagePromptTemplate(system_message_prompt_string, []string{"season", "hobbies", "dollars"})
// Create a human prompt with the request that a human would have
human_message_prompt_string := "write a travel itinerary for me"
human_message_prompt := prompts.NewHumanMessagePromptTemplate(human_message_prompt_string, []string{})
// Create a chat prompt consisting of the system messages and human messages
// At this point, we will also inject the values into the prompts
// and turn them into message content objects which we can feed through
// to our LLM
chat_prompt := prompts.NewChatPromptTemplate([]prompts.MessageFormatter{system_message_prompt, human_message_prompt})
vals := map[string]any{
"season": season,
"budget": budget,
"hobbies": strings.Join(hobbies, ","),
}
msgs, err := chat_prompt.FormatMessages(vals)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error: %v", err)
return
}
content := []llms.MessageContent{
llms.TextParts(msgs[0].GetType(), msgs[0].GetContent()),
llms.TextParts(msgs[1].GetType(), msgs[1].GetContent()),
}
// Invoke the LLM with the messages which
completion, err := llm.GenerateContent(ctx, content)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error: %v", err)
return
}
v.Idea = completion.Choices[0].Content
v.Completed = true
log.Printf("Generation for %s is done!", v.Id)
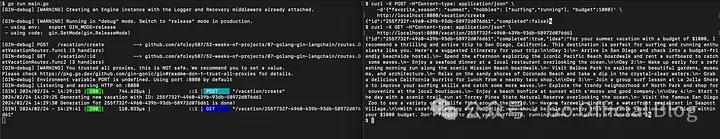
}所有的組件都已經構建好了,讓我們運行它吧!讓我們打開兩個終端:
# 導入你的 openAI API Key
$ export OPENAI_API_KEY=sk...
$ go run main.go然后測試:
$ curl -X POST -H"Content-type: application/json" \
-d'{"favorite_season": "summer", "hobbies": ["surfing","running"], "budget":1000}' \
http://localhost:8080/vacation/create可以看到接口輸出:

參考資料[1]
Gin: https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin[2]
LangChain: https://www.langchain.com/